Google has hundreds of search algorithm updates every year, with a handful of Core updates each year. These Core updates tend to be confirmed, but no specifics are given out on what they include and how they could impact brands or the SERPs (Search Engine Landing Pages). But every now and then, Google launches a major algorithm update which, in some cases, can change the whole search landscape and how brands carry out their SEO strategies.
What is an algorithm update?
Google’s algorithm updates are when Google changes its search engine to help improve user experience and quality of searches. Google is constantly changing and updating its algorithm, whether that’s with small everyday updates, broader core updates or much larger updates that have a significant impact on the search engine.
Some of the biggest and most impactful updates include:
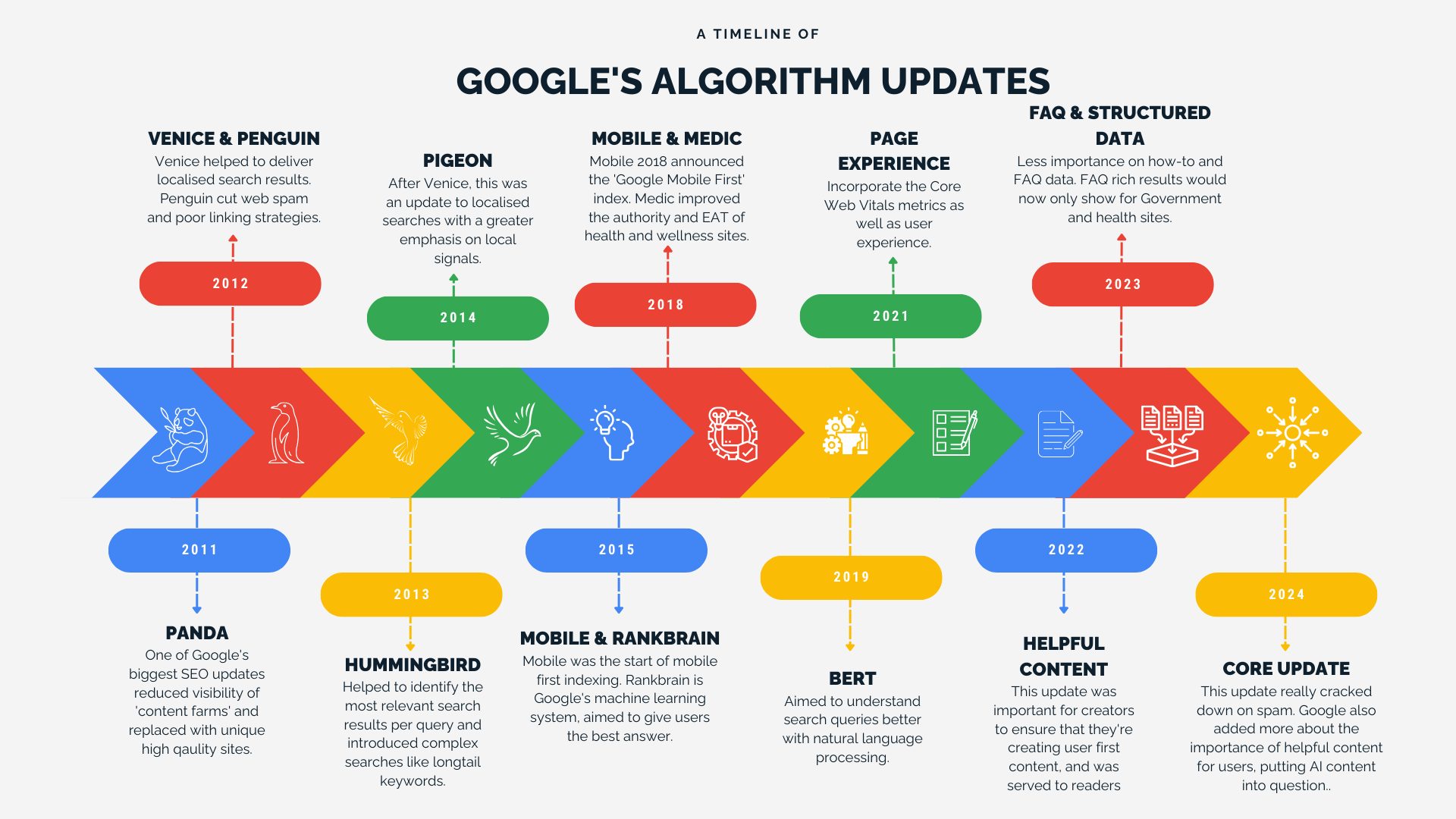
2011: Panda
This was one of the biggest Google algorithm updates that completely changed the SEO industry, as well as affecting 12% of all queries. The key aim was to decrease the visibility of low quality and thin spammy pages, such as those referred to as ‘content farms’, ensuring users would get to unique high quality and relevant sites from the SERPs.
2012: Venice
A huge change to the local search landscape, Venice helped deliver more localised results to people searching, while also using local search data. Google could then identify local user intent and helped pave the way for local businesses to grow.
2012: Penguin
This was another update for the SEO history books. The Penguin update’s aim was to cut web spam and what is now referred to as ‘black hat’ SEO tactics, such as poor linking strategies, keyword stuffing and cloaking. Paid backlinks, in particular were penalised and linkfarm sites were negatively impacted.
2013: Hummingbird
Another key update that changed the Google landscape. The Hummingbird update helped identify the most relevant search results for each query, as well as introduced more complex searches, such as longer tail and conversational queries. After this, Google was able to use context more and provide much more relevant results to users.
2014: Pigeon
The next stage after Venice introduced the localisation of SEO, the Pigeon update refined local searches even more. There was greater emphasis on local signals and an improvement in local search results. Users could now see results closer to them rather than just on a city-wide level.
2015: Mobile
The start of mobile first indexing encouraged mobile friendly websites and awarded them higher rankings on mobile searches.
2015: Rankbrain
Rankbrain is Google’s machine learning system and aimed to give users the best answer, while also understanding the search intent. This works for both new and existing search queries. This is an update that is still vital to Google and has been dubbed as one of the most influential ranking factors.
2018: Mobile
The first of two mobile updates this year, the Mobile First update showed the changing landscape with the increase in mobile usage, with Google announcing a ‘mobile first’ index. The aim of this was to encourage sites to be aimed at mobile usage.
The second update was around mobile site speed, making page speed a ranking factor on mobile, where previously it was only on desktop.
2018: Medic
While not just focussing on medical sites, the Medic update did affect the health, wellness and finance industry the most. Google wanted experts to be sharing expertise advice and sites to show that they were an authority in these spaces. Sites with high levels of EAT (Expertise – Authority – Trust) performed well following on from this.
Most of the webpages affected by this update were Your Money, Your Life (YMYL) pages.
2019: BERT
Hailed as one of the biggest changes to Google in recent years, the BERT model aimed to understand search queries even better with natural language processing. It allowed Google to interpret natural language searches and to understand wider context and more complex searches.
2021: Page Experience
After a year of warning, the Page Experience update started rolling out, taking over two months to fully roll out. This update now incorporated the Core Web Vitals metrics as well as user experience. This initially rolled out over mobile and incorporated desktop the following year, with quick to load sites and clear navigations being key to performing well in SERPs.
2022: Helpful Content
The Helpful Content update was important for creators to ensure that they’re creating user first content, making sure that any content being served to users is high quality and useful to readers. Factors such as the user experience, how useful a piece is and the quality of it all contribute towards the ranking of that page.
2023: FAQ and How-To Structured Data Update
In mid-2023, Google announced that it would be giving less importance to the FAQ and how-to structured data. While there was no negative impact on sites that already have this in place, FAQ rich results would now only be shown for authoritative Government and health sites. Despite this, it is still recommended to include FAQ content, where relevant, as it is still useful content for users.
2024: Core Update
March 2024 saw one of Google’s larger core updates. This was described as more complex than their usual updates and took over a month to fully roll out. This update focused more on spam and really cracked down on the likes of spam sites. Further to this, Google added more about the importance of helpful content for users, putting AI content into question.
What’s next?
Since the traction around AI has been picking up from late 2022, Google has announced the launch of its new Search Generative Experience, currently only rolled out in the US. The Generative AI will make searching even easier for users, answering more and more complex queries as well as the option to add follow-up questions. Though this isn’t fully rolled out, it’s a taster of things to come and where Google is heading.
To find out more about how Google’s algorithms affect your site or if you’ve negatively been hit by an update, get in touch with our Digital team now.